System Restore (restorept.api) is a new Windows XP feature that's similar to "Last Known Configuration." However, System Restore maintains multiple restore points instead of one last restore point. The user can manually create restore points, or System Restore can keep restore points during the following operations:
Installing new software, if the application uses a current installer that is System Restore-compliant, Using AutoUpdate, During a restore operation, During a Microsoft backup or recovery operation, Installing an unsigned driver, Automatically following 24 hours of inactivity.
By default, System Restore monitors all partitions. So, for example, if you delete an executable file, you can have the system state revert to a specific restore point to recreate or repair the executable file. When you revert to a restore point, however, you lose all changes since that point, except for changes to files in the My Documents folder and documents you've created with applications such as Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel.
If you use System Restore and don't like the new system state, you can undo the process and restore the machine to the system state it had before you ran System Restore. Alternatively, you can run System Restore to change the system state to a different restore point.One of the best features of Windows ME, XP, or Windows Vista is the System Restore option, however if a virus infects a computer with this operating system the virus may be accidentally backed up because of this feature. In order to completely remove a virus on these operating systems, you should disable System Restore before cleaning the system, then reenable it after the system is clean. Follow the instructions below to disable System Restore
Disabling System Restore on Windows ME
1. Click Start, Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the System icon. The System Properties dialog box appears.
NOTE: If the System icon is not visible, click "View all Control Panel options" to display it.
3. Click the Performance tab, and then click File System.
4. Click the Troubleshooting tab, and then check Disable System Restore.
5. Click OK. Click Yes, when you are prompted to restart Windows.
Once you have cleaned the virus or other problem from the computer, reenable System Restore by following these directions
To enable Windows Me System Restore:
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click System, and then click the Performance tab.
3. Click File System, and then click the Troubleshooting tab.
4. Uncheck Disable System Restore.
5. Click OK. Click Yes, when you are prompted to restart Windows.
Disabling System Restore on Windows XP
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- You must be logged in as an Administrator to do this. If you are not logged in as an Administrator, the System Restore tab will not be displayed.
- Turning off System Restore will clear out all previous restore points.
To turn off Windows XP System Restore:
NOTE: These instructions assume that you are using the default Windows XP Start Menu and have not changed to the Classic Start menu. To re-enable the default menu, right-click Start, click Properties, click Start menu (not Classic) and then click OK.
1. Click Start.
2. Right-click the My Computer icon, and then click Properties.
3. Click the System Restore tab.
4. Check "Turn off System Restore" or "Turn off System Restore on all drives" as shown in this illustration:
5. Click Apply.
6. When turning off System Restore, the existing restore points will be deleted. Click Yes to do this.
7. Click OK.
8. Proceed with what you need to do; for example, virus removal. When you have finished, restart the computer and follow the instructions in the next section to turn on System Restore.
To turn on Windows XP System Restore:
1. Click Start.
2. Right-click My Computer, and then click Properties.
3. Click the System Restore tab.
4. Uncheck "Turn off System Restore" or "Turn off System Restore on all drives."
5. Click Apply, and then click OK.
Starting System Restore From a Command Prompt in Windows XP
1. Restart your computer or turn the computer on
2. Start tapping the F8 key. The Windows Advanced Options Menu appears. If you begin tapping the F8 key too soon, some computers display a "keyboard error" message. To resolve this, restart the computer and try again.
3. Select the "Safe Mode with Command Prompt
option" and press Enter
4. Log on to the computer with an administrator account
5. Type the following at the command prompt and press Enter
%systemroot%\system32\restore\rstrui.exe6. Follow the onscreen instructions to restore your computer to an earlier time.
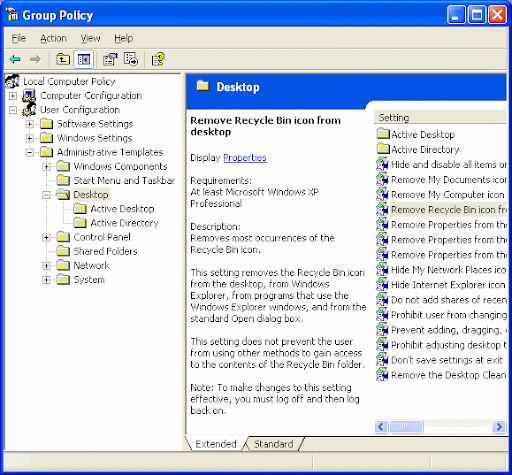
Re-enabling System Restore in Windows XP via the Group Policy Editor
In some cases, System Restore is disabled via the Group Policy Editor. In these cases, System Restore does not show up as a tab under My Computer Properties in Windows XP
. If it doesnt show up, the question becomes how do you turn it on in the first place. To re-enable System Restore via the Group Policy Editor, follow these directions:
1) Start the Group Policy Editor by clicking on Start, Run and typing gpedit.msc in the Run box and pressing Enter
2) In the left hand column, click on Computer Configuration, Administrative Templates, System, System Restore
3) In the right hand column, set Turn off System Restore and Turn off Configuration to Disable
4) Minimize the Group Policy Editor
5) Right click on My Computer and Select Manage
6) In the right hand column, double click on Services and Applications, then Services
7) Find the System Restore Service and double-click to open
8) On the General tab set [Startup Type] to Automatic using the drop down list
9) Click the Start button to start the service
10) Close the Computer Management console
11) Maximize the Group Policy Editor and set Turn off System Restore and Turn off Configuration to Not Configured
12) Close Group Policy Editor and reboot the system.
13) Once the system is rebooted, Click on Start, Right-click on My Computer, click on Properties and the System Restore tab should appear again.
An alternative to the usual method of enabling and disabling Windows XP's System Restore feature is to use the registry. To use this alternative, perform the following steps: Start the registry editor (regedit.exe).
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore.
If a "DisableSR" value doesn't exist, go to the Edit menu, select New, DWORD value, and create the value. Set the value to 1 to disable System Restore or 0 to enable System Restore.
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\sr to prevent the System Restore service from starting.
Double-click Start, and set the value to 4 to stop the service from starting or to 0 for normal startup. Close the registry editor. 
Disabling System Restore on Windows Vista
To turn off Windows Vista System Restore:
1. Click Start.
2. Right-click the Computer icon, and then click Properties.
3. Click on System Protection under the Tasks column on the left side
4. Click on Continue on the "User Account Control" window that pops up
5. Under the System Protection tab, find Available Disks
6. Uncheck the box for any drive you wish to disable system restore on
7. When turning off System Restore, the existing restore points will be deleted. Click "Turn System Restore Off" on the popup window to do this.
8. Click OK
9. When you have finished, restart the computer and follow the instructions in the next section to turn on System Restore.
To turn on Windows Vista System Restore:
1. Click Start.
2. Right-click the Computer icon, and then click Properties.
3. Click on System Protection under the Tasks column on the left side
4. Click on Continue on the "User Account Control" window that pops up
5. Under the System Protection tab, find Available Disks
6. Place a checkmark in the box for any drive you wish to enable System Restore on
7. Click OK
 To enable the Windows 7 administrator account:
To enable the Windows 7 administrator account: